Why Users Need a Trust DNS?
Why Users Need a Trust DNS
In today’s digital landscape, the Domain Name System (DNS) plays a crucial role in connecting users to the internet. A reliable and secure DNS is vital for ensuring that users access the right websites and services without interference or malicious attacks. Trust DNS has emerged as a solution that prioritizes security, privacy, and reliability. In this blog, we will dive deep into why users need a trust DNS, explore its benefits, and how it can enhance online safety and user experience.
Understanding DNS and Trust DNS
Before we delve into why users need a trust DNS, let’s first define a few key terms.
DNS (Domain Name System) is the system responsible for translating human-readable domain names (like www.example.com) into IP addresses that computers can understand. Without DNS, users would have to memorize complex IP addresses for every website they want to visit. DNS servers are the backbone of the internet, enabling seamless access to websites and services.
Trust DNS is a DNS service focused on providing security, privacy, and reliability to users. It prevents common DNS-related threats, such as DNS hijacking, spoofing, and phishing, ensuring a safer online experience. Trust DNS also enhances privacy by minimizing data collection and preventing third-party tracking.
Key Reasons to Use Trust DNS
1. Enhanced Security Against DNS Hijacking and Spoofing
DNS hijacking and spoofing are common cyberattacks in which hackers manipulate DNS requests to redirect users to malicious websites or steal sensitive information. If a user’s DNS is not secure, attackers can exploit vulnerabilities, leading to significant data breaches and identity theft. A trusted DNS actively prevents these attacks by offering encrypted DNS queries and response authentication. This ensures that users are always directed to the correct websites.
2. Protection Against Phishing Attacks
Phishing is a widespread tactic where attackers create fake websites that look identical to legitimate ones. By tricking users into entering sensitive information like passwords and credit card details, phishing scams can result in massive financial loss. DNS solutions offer filtering capabilities that block access to known malicious websites, safeguarding users from falling victim to phishing attacks.
3. Privacy Protection and Data Encryption
Another key feature of DNS is its emphasis on privacy. Many free DNS services, such as those offered by ISPs or search engines, collect and log user data, including browsing habits, to sell to third parties or for targeted advertising. Trust DNS services, however, respect user privacy by not logging queries and encrypting DNS traffic, preventing unauthorized access to browsing data. DNS encryption helps prevent third parties, such as hackers or governments, from eavesdropping on DNS queries.
4. Prevention of Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
Man-in-the-middle attacks occur when a hacker intercepts communication between a user and a website. This type of attack can be devastating, as it enables attackers to steal sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and financial details. A trust DNS incorporates DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions), which adds an additional layer of authentication to DNS queries, ensuring that the data received by the user is legitimate and has not been tampered with during transmission.
5. Improved Internet Speed and Performance
Slow internet can be frustrating, especially when it comes to streaming or gaming. While the quality of your internet connection plays a major role, DNS servers can also affect performance. A poorly optimized DNS can slow down the time it takes to resolve domain names, leading to delays in accessing websites. Trust DNS services often feature optimized servers and smart routing technologies, ensuring faster query resolution and better overall internet performance.
6. Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
Some DNS services enable users to bypass geo-restrictions placed on certain content or websites. For instance, streaming services may block certain shows or movies based on your location. Trust DNS services provide access to international content by bypassing these restrictions while ensuring that the connection remains secure and encrypted. However, users should always ensure they are following local regulations when using such features.
7. Increased Reliability and Uptime
DNS outages can render websites inaccessible, disrupting business operations and frustrating users. Unlike traditional DNS services that may experience downtime, trust DNS solutions offer increased reliability by using redundant infrastructure. This ensures that even if one server goes down, others can handle the traffic, ensuring continuous access to websites and services.
Trust DNS and IoT Security
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has introduced new security challenges. Many IoT devices connect to the internet using traditional DNS, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks. Since IoT devices often lack robust security protocols, they can be easily compromised through DNS-based attacks. A trust DNS can provide an additional layer of protection for IoT devices by preventing DNS spoofing and hijacking. Moreover, with its encryption and authentication features, trust DNS ensures that IoT devices communicate only with legitimate servers.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Trust DNS
1. Encryption Standards
Not all DNS services offer encryption, and this should be a primary factor in choosing a trust DNS. Look for services that support DNS over HTTPS (DoH) or DNS over TLS (DoT). These protocols ensure that DNS queries are encrypted, preventing third parties from intercepting or manipulating the data.
2. No-Logging Policy
Choose a trust DNS provider with a strict no-logging policy, meaning that they do not store any user data or browsing history. This ensures that your online activities remain private and cannot be sold to third parties or compromised in a data breach.
3. Speed and Server Locations
Speed is a crucial factor in DNS resolution. Trust DNS providers with a large number of servers spread across different regions tend to offer better performance. Look for a service with a global presence and optimized query resolution to ensure the best experience.
4. Customizability and Filtering Options
A good trust DNS service should offer users the ability to customize their settings, including blocking specific types of websites or content. For families or businesses, content filtering options can provide an additional level of protection, ensuring that malicious or inappropriate content is blocked automatically.
The Future of DNS Security
As cyber threats continue to evolve, so too must our security solutions. Trust DNS represents the next step in the evolution of DNS security, offering enhanced protection and privacy in an increasingly dangerous digital landscape. Moreover, with the continued growth of IoT devices and cloud computing, the demand for secure DNS solutions will only increase.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a trust DNS offers users enhanced security, privacy, and reliability, making it a critical tool in protecting against DNS-related cyberattacks. From preventing phishing and MITM attacks to ensuring data privacy and fast internet speeds, trust DNS services provide a comprehensive solution for a safer and more seamless online experience. Given the growing threats to online security, users can no longer afford to rely on traditional DNS services.
For businesses and individuals looking to enhance their DNS security and enjoy the benefits of a trust DNS, Hyper ICT Oy in Finland offers tailored solutions designed to meet your specific needs. Contact them today to learn more about how trust DNS can safeguard your online activities.
Contact Hyper ICT

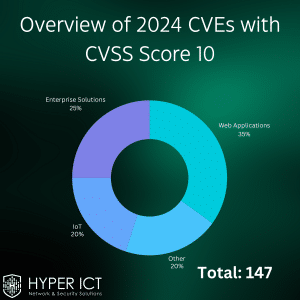 Overview of 2024 CVEs with CVSS Score 10
Overview of 2024 CVEs with CVSS Score 10